Thank You for Asking:
following the welder’s recommendations for other amorphous thermoplastics.
- Read more about Thank You for Asking:
- Log in or register to post comments
Mold design—critical factor #5
Tips for a clean release
 The coefficient of friction of copolyesters such as Eastman Tritan™ copolyester is at its highest near the heat deflection temperature (HDT) of the material—and competitive materials generally freeze at a higher temperature than Tritan. Keep this in mind if you’re repurposing a mold that was originally designed for the cooling temperature of another plastic. Parts molded with Tritan must be adequately cooled to withstand ejection forces during demolding.
The coefficient of friction of copolyesters such as Eastman Tritan™ copolyester is at its highest near the heat deflection temperature (HDT) of the material—and competitive materials generally freeze at a higher temperature than Tritan. Keep this in mind if you’re repurposing a mold that was originally designed for the cooling temperature of another plastic. Parts molded with Tritan must be adequately cooled to withstand ejection forces during demolding.
Three mold design and maintenance factors can also help ensure a clean and efficient release:
Draft—Part design features with minimal draft, such as long cores and deep ribs, often result in high ejection forces. The Eastman Design Services team recommends that all wall surfaces have a minimum draft angle of 1° in the direction of draw.
Three mold design and maintenance factors can also help ensure a clean and efficient release:
Draft—Part design features with minimal draft, such as long cores and deep ribs, often result in high ejection forces. The Eastman Design Services team recommends that all wall surfaces have a minimum draft angle of 1° in the direction of draw.
- Read more about Mold design—critical factor #5
- Log in or register to post comments
Designing Disinfectant-Ready Medical Devices
Are the devices you design ready for aggressive medical disinfectants?
 The designer is the point where innovative creativity crashes head-on into the real-world needs of durable functionality in a health care environment.
The designer is the point where innovative creativity crashes head-on into the real-world needs of durable functionality in a health care environment.
Unfortunately, many device housings and hardware designed just a few years ago were made with materials that lack the right combination of impact strength and chemical resistance. They crack, craze, and ultimately fail when challenged by the increased use of aggressive medical disinfectants—combined with the applied stress of greater portability.
Connecting the dots between design flexibility, chemical resistance, and impact strength is critical for selecting the best material for reliable clear and opaque medical devices. That’s why Eastman created a 60-minute webinar to provide new information about:
Patient safety and HAI prevention
 The designer is the point where innovative creativity crashes head-on into the real-world needs of durable functionality in a health care environment.
The designer is the point where innovative creativity crashes head-on into the real-world needs of durable functionality in a health care environment.Unfortunately, many device housings and hardware designed just a few years ago were made with materials that lack the right combination of impact strength and chemical resistance. They crack, craze, and ultimately fail when challenged by the increased use of aggressive medical disinfectants—combined with the applied stress of greater portability.
Connecting the dots between design flexibility, chemical resistance, and impact strength is critical for selecting the best material for reliable clear and opaque medical devices. That’s why Eastman created a 60-minute webinar to provide new information about:
Patient safety and HAI prevention
- Read more about Designing Disinfectant-Ready Medical Devices
- Log in or register to post comments
Mold design — critical factor #4
Gate style, location, and size
 The gate is where it all comes together in injection molding. Mold design and part design. The molten resin and the solid molded product. Aesthetics and mechanical performance.
The gate is where it all comes together in injection molding. Mold design and part design. The molten resin and the solid molded product. Aesthetics and mechanical performance.
Skillful decisions about gate style, location, and size early in the mold and part design process can pay big dividends when it is time to start molding parts. And the benefits pay off in greater part performance and reliability.
Overriding considerations—aesthetics and mechanical properties
Regardless of gating type, location, or size, these two factors will drive most decisions made regarding gating:
Aesthetics
The gate on an injection molded part leaves a “witness,” or a vestige, where the part is separated from the runner system. This is considered an appearance defect and is typically hidden in an area of the part where it will not be obvious.
Skillful decisions about gate style, location, and size early in the mold and part design process can pay big dividends when it is time to start molding parts. And the benefits pay off in greater part performance and reliability.
Overriding considerations—aesthetics and mechanical properties
Regardless of gating type, location, or size, these two factors will drive most decisions made regarding gating:
Aesthetics
The gate on an injection molded part leaves a “witness,” or a vestige, where the part is separated from the runner system. This is considered an appearance defect and is typically hidden in an area of the part where it will not be obvious.
- Read more about Mold design — critical factor #4
- Log in or register to post comments
Overmolding for soft-touch designs
New self-bonding LSR technology created to optimize Eastman Tritan™ copolyesters
The medical industry has a great and growing demand for innovative soft-hard designs in devices, housings, and other equipment. A recent advance in liquid silicone rubber (LSR) technology makes it easier to satisfy this demand with medical grades of Eastman Tritan™ copolyester.
The advantages of Tritan are well-known to readers of this blog. Medical grades of Tritan offer a unique combination of properties including:
• Outstanding resistance to medical disinfectants and solvents
• Excellent impact strength and durability
• Made without BPA and halogens
• Excellent clarity and color retention after sterilization by ethylene oxide (EtO),
e-beam, and gamma irradiation

The medical industry has a great and growing demand for innovative soft-hard designs in devices, housings, and other equipment. A recent advance in liquid silicone rubber (LSR) technology makes it easier to satisfy this demand with medical grades of Eastman Tritan™ copolyester.
The advantages of Tritan are well-known to readers of this blog. Medical grades of Tritan offer a unique combination of properties including:
• Outstanding resistance to medical disinfectants and solvents
• Excellent impact strength and durability
• Made without BPA and halogens
• Excellent clarity and color retention after sterilization by ethylene oxide (EtO),
e-beam, and gamma irradiation
- Read more about Overmolding for soft-touch designs
- Log in or register to post comments
Mold design — critical factor #3
Fill pressure and fill pattern
Fill pressure and fill pattern go hand in hand.
Just as mold design is inextricably linked to part design, reasonable fill pressure and reasonable fill pattern should be evaluated together.
Reasonable fill pressure—excessive fill pressure can create several problems:
• High clamp tonnage requirements
• Reduced life of mold components—due to high stress loading
- Read more about Mold design — critical factor #3
- Log in or register to post comments
Polymer selection for durables applications
Selecting the best grade for food contact and non-food contact applications
Brand owners and design engineers continue to find new ways to use Eastman Tritan™ copolyesters in a wide range of food contact and non-food contact applications.
Its unique combination of clarity, durability, hydrolytic stability, and heat and chemical resistance makes Tritan ideal for many applications, including:
Food contact applications
• Commercial housewares
• Sports bottles
• Small appliances
• Infant care
• Water filtration
Non-food contact applications
• Appliances
• Leisure and safety
• Ophthalmics
• Oral care
• Tools
• In-mold decorations
Starting with your specific needs, Eastman can provide technical expertise and support to help determine the best grade of Tritan for your application.
Brand owners and design engineers continue to find new ways to use Eastman Tritan™ copolyesters in a wide range of food contact and non-food contact applications.
Its unique combination of clarity, durability, hydrolytic stability, and heat and chemical resistance makes Tritan ideal for many applications, including:
Food contact applications
• Commercial housewares
• Sports bottles
• Small appliances
• Infant care
• Water filtration
Non-food contact applications
• Appliances
• Leisure and safety
• Ophthalmics
• Oral care
• Tools
• In-mold decorations
Starting with your specific needs, Eastman can provide technical expertise and support to help determine the best grade of Tritan for your application.
- Read more about Polymer selection for durables applications
- Log in or register to post comments
Mold design—critical factor #2
Thermal control of cavity surfaces
 Thermal control is critical for injection molding Eastman Tritan™ copolyester. Keeping temperatures cooled below the heat deflection temperature (HDT) of Tritan helps ensure successful demolding with no dragging or sticking of parts. Preparing a cooling strategy early in the tool design process can pay big dividends in cycle time and processability.
Thermal control is critical for injection molding Eastman Tritan™ copolyester. Keeping temperatures cooled below the heat deflection temperature (HDT) of Tritan helps ensure successful demolding with no dragging or sticking of parts. Preparing a cooling strategy early in the tool design process can pay big dividends in cycle time and processability.
One key to keeping it cool—just add water.
It’s not that simple. But providing ample and well-positioned cooling water channels is critical to controlling the temperature of the cavity surface and the resin in the mold. Here’s why controlling resin temperature is important: as the resin approaches HDT, it becomes sticky (the coefficient of friction increases) and parts cannot be ejected efficiently.
One key to keeping it cool—just add water.
It’s not that simple. But providing ample and well-positioned cooling water channels is critical to controlling the temperature of the cavity surface and the resin in the mold. Here’s why controlling resin temperature is important: as the resin approaches HDT, it becomes sticky (the coefficient of friction increases) and parts cannot be ejected efficiently.
- Read more about Mold design—critical factor #2
- Log in or register to post comments
Why specify medical grade polymers
Two words: confidence and compliance
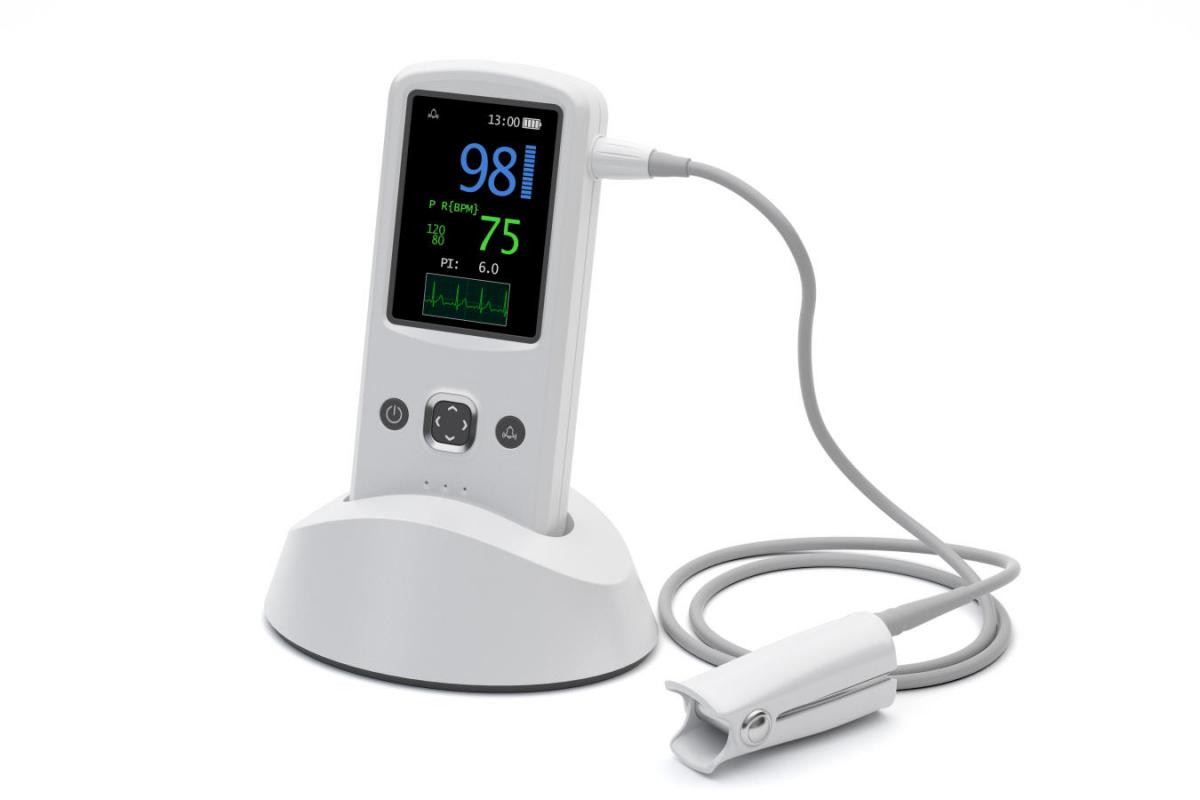
It is critical for designers of innovative medical devices and packaging to have access to high-performance medical grade materials.
To ensure patient safety and long-lasting reliability, manufacturers depend on medical grade material suppliers like Eastman—not only to provide advanced, high quality raw materials but also to have capabilities and systems that help comply with medical protocols and regulations.
Manufacturers who specify medical grades of clear or opaque Eastman Tritan™ copolyester* know that Eastman will provide a high level of support throughout the regulatory journey to commercialization of a new product. Eastman’s world of experience helps ensure confidence and compliance in the areas of:

It is critical for designers of innovative medical devices and packaging to have access to high-performance medical grade materials.
To ensure patient safety and long-lasting reliability, manufacturers depend on medical grade material suppliers like Eastman—not only to provide advanced, high quality raw materials but also to have capabilities and systems that help comply with medical protocols and regulations.
Manufacturers who specify medical grades of clear or opaque Eastman Tritan™ copolyester* know that Eastman will provide a high level of support throughout the regulatory journey to commercialization of a new product. Eastman’s world of experience helps ensure confidence and compliance in the areas of:
• Biocompatibility—selected tests from the FDA-Modified ISO-10993, Part 1 “Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices”
- Read more about Why specify medical grade polymers
- Log in or register to post comments
Mold Design- critical factors #1
Factor #1—Polymer melt residence time
 Mold design goes hand in hand with part design to determine the manufacturability of a product. One factor that is critical to manufacturability—as well as to preserving the performance characteristics of the material being used—is polymer melt residence time.
Mold design goes hand in hand with part design to determine the manufacturability of a product. One factor that is critical to manufacturability—as well as to preserving the performance characteristics of the material being used—is polymer melt residence time.
In this blog, the first of a five-part series discussing critical factors of mold design, we answer these questions about melt residence time:
Melt residence time—know when enough is enough (and why)
In this blog, the first of a five-part series discussing critical factors of mold design, we answer these questions about melt residence time:
• What is melt residence time?
• How does it affect the integrity of a polymer?
• How does this relate to Eastman Tritan™ copolyester?
• What is the residence time recommendation for Tritan?
• How does this relate to Eastman Tritan™ copolyester?
• What is the residence time recommendation for Tritan?
Melt residence time—know when enough is enough (and why)
- Read more about Mold Design- critical factors #1
- Log in or register to post comments




 Close
Close


