Jul
15
15

Compared to gamma radiation, e-beam radiation typically costs less due to higher dose rates that reduce the time of exposure at the same target dose. The shorter exposure time also minimizes the oxidation reactions that can occur at the polymer surface, resulting in less effect on resin properties than with gamma radiation.
To determine the effects of e-beam radiation on Tritan and other transparent medical polymers, Eastman conducted a series of studies that measured color shifting and physical property retention. Specific products tested are shown here:
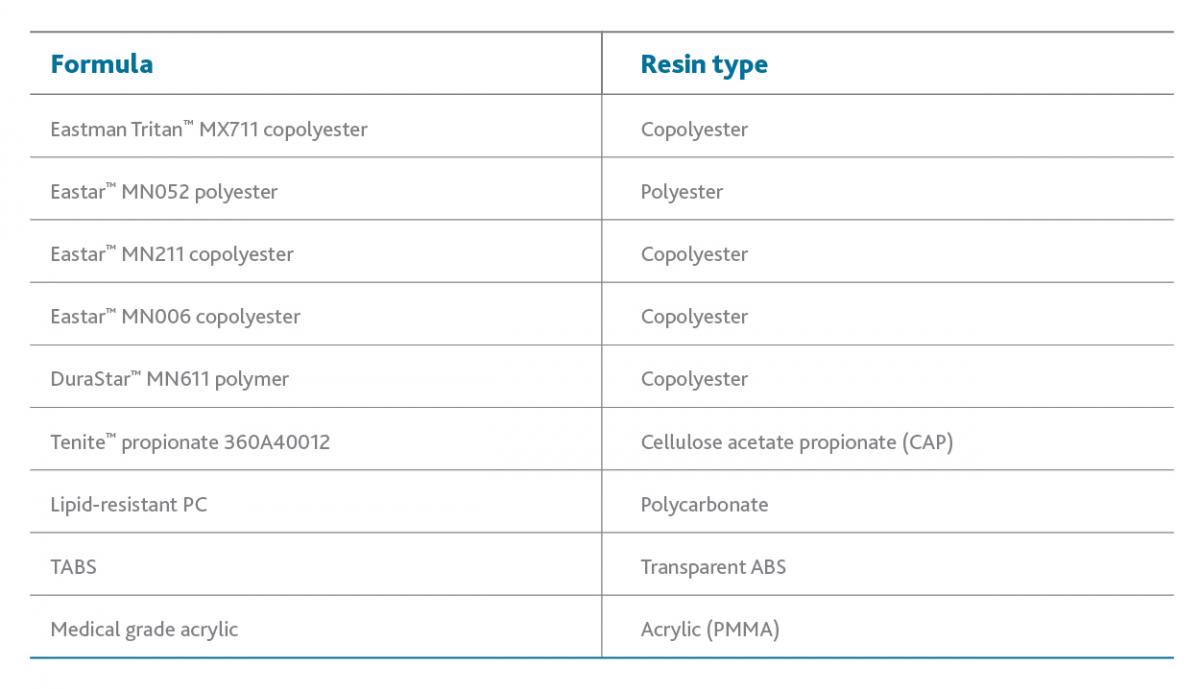
Optical properties
Samples were exposed to e-beam radiation (25 and 50 kGy) and then stored in darkness. Their color was measured at days 3, 7, 14, and 42 using HunterLab UltraScan™ Sphere 8000 and the CIE L*, a*, b* color scale. (Samples were stored in darkness and only exposed to light for color measurement.)
Samples were exposed to e-beam radiation (25 and 50 kGy) and then stored in darkness. Their color was measured at days 3, 7, 14, and 42 using HunterLab UltraScan™ Sphere 8000 and the CIE L*, a*, b* color scale. (Samples were stored in darkness and only exposed to light for color measurement.)
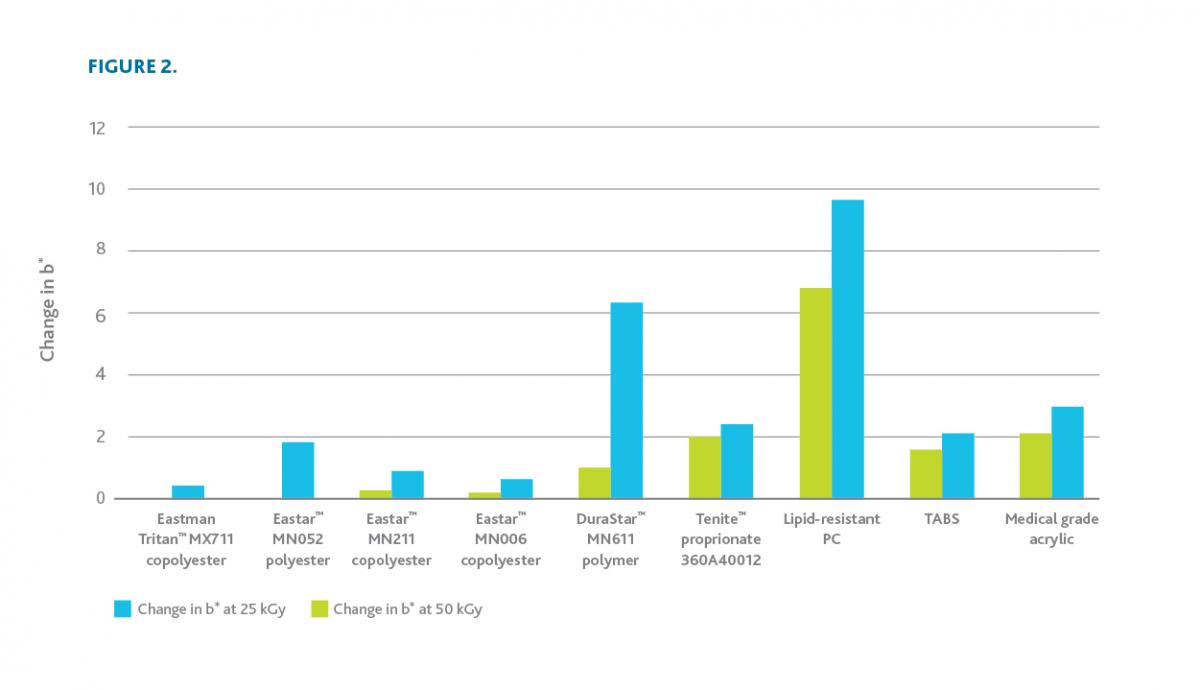
Figure 2 shows the difference in b* color values between unexposed samples and sterilized samples at day 42—after e-beam radiation at both 25 and 50 kGy.
Figure 2. Change in b* color 42 days after e-beam radiation—25 and 50 kGy

Physical properties were measured before and after e-beam sterilization at 25 and 50 kGy. No physical property degradation was noted for Tritan MX711 or the other resins tested. The polyesters and copolyesters in the study showed no statistical change in molecular weight, although Tenite propionate 360 did show a loss of molecular weight, as expected from an aliphatic polymer.
Read the complete details of these studies here.
Read the complete details of these studies here.
Blog categories:
Jun
17
17

Using overmolded soft-touch materials can provide many functional and decorative benefits to items made from rigid thermoplastics. Eastman Tritan™ copolyester demonstrates exceptional adhesion with commercial grades of TPE. When selecting the TPE you want to use, make sure it is formulated for use with a copolyester substrate.
Consider these factors for part design:
For more information about using Tritan in secondary operations, download our Secondary Operations Guide.
Consider these factors for part design:
- Optimize part and TPE thickness for adhesion and dimensional stability. If the TPE thickness is in excess of the Tritan part thickness, you could see warpage when you remove it from the mold. Use a substrate thickness twice that of the TPE.
- Incorporate mechanical interlocks to improve TPE adhesion and promote part durability. Mechanical interlocks are important for thin TPE layers and very demanding fitness-for-use requirements.
- Use flow-through designs to improve adhesion and durability. This is especially beneficial for designs incorporating soft-touch features on multiple surfaces.
- Ensure the edge of the TPE is flush with or below the level of the non-overmolded section of the rigid substrate. This will minimize the potential for peeling or delamination.
For more information about using Tritan in secondary operations, download our Secondary Operations Guide.
Blog categories:
May
13
13

We know that material choice is a crucial component of any medical device or device housing. When you’re deciding what medical grade polymer you need for your next project, consider these criteria:
- Does it make the grade?
- Will it match the application?
When matching a medical grade of Eastman Tritan™ copolyester to your needs, keep in mind that each medical application has different performance priorities. For example, while opaque medical housings demand a greater level of durability, chemical resistance, color stability, and heat resistance, clear applications—such as fluid management and IV components—also place a high value on clarity.
Eastman provides a range of medical grades of Tritan. Here are some outstanding properties of our clear and opaque formulations of the polymer:
Clear formulations of Tritan:
- Offer greater toughness, heat resistance, processability, and design freedom compared with other copolyesters
- Retain clarity, color stability, and functional integrity after sterilization
- Provide outstanding chemical resistance to lipids, IPA, disinfecting agents, and bonding solvents and adhesives
- Provide excellent functionality and reliability to device housings
- Ensure compatibility with the new reality of aggressive disinfection and the daily impact stresses that come with greater portability
- Retain color and functionality following sterilization with gamma and e-beam irradiation
- Offer reliable color matching—drawing on the expertise of the Eastman Color Technology Center
- Provide flame-retardant properties
Blog categories:
Apr
15
15

What makes for effective molding of Eastman Tritan™ copolyester? Reviewing all aspects of design—from concept to secondary operations—early on in the process is crucial to end-stage success.
Tooling design review is one important step in the process that will help determine what type of gating system is right for your device. Here are four quick tooling design tips for injection molding with Tritan:
By collaborating with our team from the get-go, you’ll be sure to see greater return on investment for your project in the end. Contact us for processing tips and more!
Tooling design review is one important step in the process that will help determine what type of gating system is right for your device. Here are four quick tooling design tips for injection molding with Tritan:
- Proper gating selection
Select a compatible gating style for the selected resin. Most conventional cold gating styles work well with Tritan copolyesters, including sub, pin, fan, edge, sprue, and diaphragm gates.
- Design tooling with good cooling/thermal control
Copolyesters require good thermal control throughout the cavity for optimal processing.
- Design tooling with a plan for venting
Poor venting can result in burn marks and incomplete fill. Suggested vent depths for Tritan copolyesters are typically 0.0005–0.0015 in.
- Design tooling with a plan for ejection
By collaborating with our team from the get-go, you’ll be sure to see greater return on investment for your project in the end. Contact us for processing tips and more!
Blog categories:
Mar
4
4

The need to mitigate infection risks and enhance patients’ safety and comfort has significantly increased the demand for higher-performing plastics with improved chemical resistance. Many polymers commonly used in drug delivery devices simply do not hold up to modern oncology chemotherapies. After exposure to chemicals in the medical environment, devices made with these polymers can experience environmental stress cracking or premature failure in the presence of applied or residual stress.
Broken devices put patients at risk. What’s more, regulatory agencies may tell manufacturers to stop using certain materials when device performance or life cycle is compromised.
For these reasons, when you are choosing materials for your medical device, evaluating polymers for chemical resistance is key. Eastman Tritan™ copolyesters have excellent overall chemical resistance and other advantages that make them superior alternatives to polycarbonate (PC) or acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) for oncology drug delivery devices.
Tritan also offers compatibility with many popular sterilization methods and has outstanding hydrolytic stability. This balance of properties makes Tritan a great choice for IV system components, blood therapy devices, and any parts that face frequent disinfection. Read more about the benefits Tritan offers devices that encounter hospital disinfectants and oncology drugs here.
Blog categories:




 Close
Close







